Smart Tables Activation & configuration
What is a Smart Table
A smart table is a table with the capacity to create and remove indexes by itself! There is no need to manually run the Analyzer since it would be automatically run.
How Smart Table works in general
Each smart table will get a score (based on Execution time, ...). This notation leads to a sorted list of tables that need to be optimized.
Activate & Define timeframe
Each time (defined by analyser.smart.scheduling.cron), the system will determine which table needs to be optimized. The whole optimization process will last a maximum of analyser.smart.scheduling.duration.minutes
The "smart table" feature is active by:
- defining a valid value in the
analyser.smart.scheduling.cron(CRON expression which defines the timelapse the whole process would be launched) and activating the analyzer in incremental mode: see
analyzer.modein Galactica.conf
Deactivation
If you want to deactivate the process of the Smart tables, define an empty value to analyser.smart.scheduling.cron
How can I set my smart criteria?
Optimization method
Define the default optimization method for all tables
Default optimization method would be defined by analyser.smart.optimizer which has to be a value defined in optimize_index.json.
By default, all tables would be optimized using the default configuration.
Set another optimization method for a table
The default value is "Default", meaning the optimization method inherits from the parameter analyser.smart.optimizer.
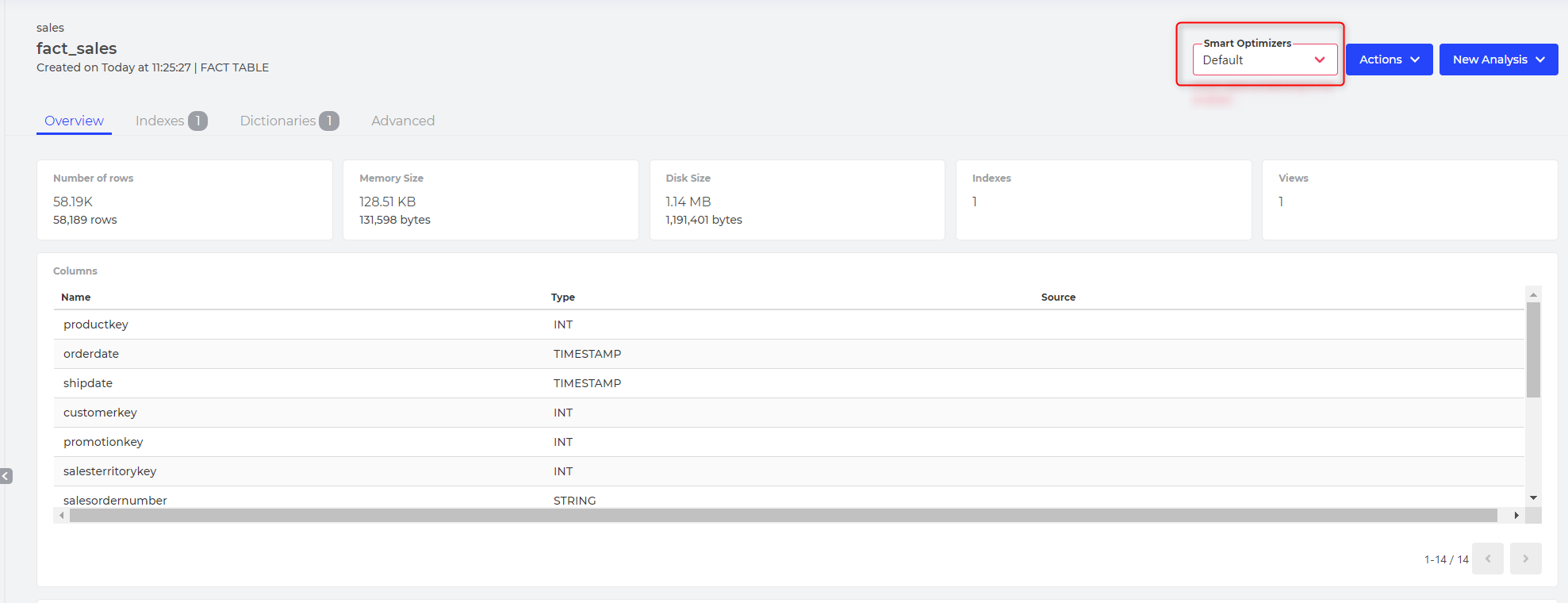
In the Developer Console, it is possible to explicitly set the optimization method to another value, even set it to None to disable the smart process on a specific table.
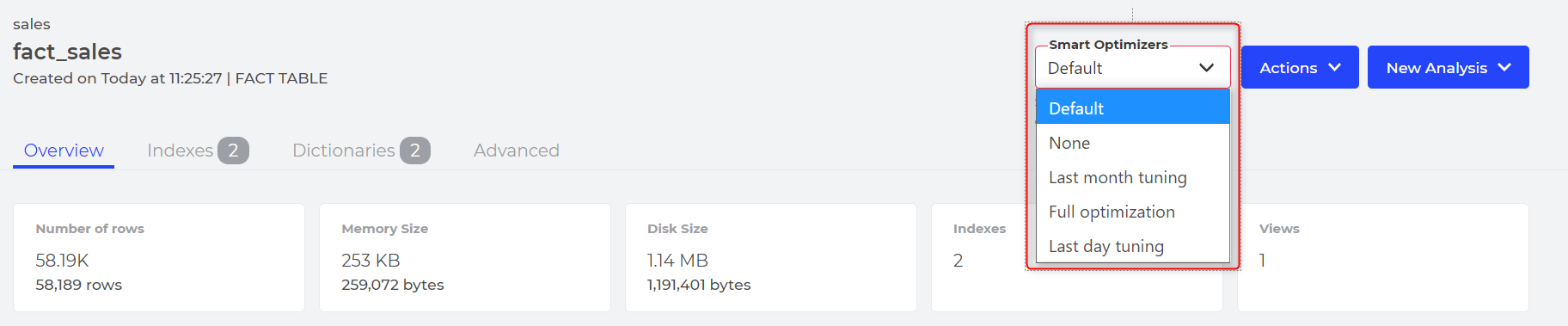
Choose (and weight) metrics to take into account
Each metric could be weighted to prioritize some characteristics that will give a score for each table. By default, all weight parameters have a value of analyser.smart.weight (default value:1), meaning that they are all as important. You can disable criteria by setting a value to 0. Each weight is an integer.
| Metric Name | associated weight parameter name |
|---|---|
| Number of queries using K-Store overall queries on the table | analyser.smart.weight.bucket |
Number of slow queries over all queries. A slow query is a query with takes more than analyser.smart.threshold.slow.ms ms to finish.CACHED queries are not taken into account. | analyser.smart.weight.speed |
| Number of queries delegated to the underlying source overall queries | analyser.smart.weight.delegate |
| Size of the table over the size of all tables | analyser.smart.weight.size |
| Number of requests on this table over the total number of queries on the cluster | analyser.smart.weight.traffic |
Metrics timeframe
For each table, metrics would be computed over a period defined by analyser.smart.metrics.days
Analyzed tables at the same time
A maximum of analyser.smart.threads tables would be analyzed and optimized at the same time.
Define Boundaries
Maximum number of indexes per table
For each table, Indexes would be added up to a limit of analyser.smart.max.indexes (default 20) indexes
if the policy of the setting does NOT allow deletion, a table with max indexes will not be taken into account for smart indexing
In any case, a table will not run the indexes creation/drop if the number of indexes will reach the max (current + to be added - to be dropped)
When time is elapsed
The whole optimization process (Analysis, Add & Drop Index) will last a maximum of analyser.smart.scheduling.duration.minutes.
The 3 steps (Analysis, Add & Drop Index) are considered as a whole process for a table.
Once the process is started for a table, it cannot be stopped. If the time elapses during one of the 3 steps of the process, the smart table process would stop without canceling ongoing operations.
Example
1. Let's say you set the following parameters
analyser.smart.weight.bucket=1analyser.smart.weight.speed=2- All other parameters are set to 0
2. and you have the following metrics for 2 tables
| Table Name | % Query in buckets | % Slow Queries |
|---|---|---|
| Table1 | 50% | 20% |
| Table2 | 30% | 30% |
3. As a result, the following scores are computed, leading to a computed rank
| Table Name | % Query in buckets | % SlowQueries | Score | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table1 | 50% | 20% | 90 = 1*50 + 2*20 | 1 |
| Table2 | 30% | 20% | 70 = 1*30 + 2*20 | 2 |
Table1 would be first optimized, then, if there is enough time left, Table2
Available scenarios
3 provided scenarios
Indexima provides 3 scenarios of optimization
Nb Days | MinHits | Index Coeff | Prejoin | Index Spec | index-hint | Action | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Last Month Tuning | 30 | 1 | 4 | True | Not Spec | TUNING | Create & Delete |
Last Day Tuning | 4 | 1 | 4 | True | Not Spec | TUNING | Create & Delete |
Full optimization | 30 | 1 | 4 | True | Not Spec | FULL | Create & Delete |
Create a new scenario
Admin users can add new scenarios. They have to fill up the optimize_index.json file. Go to optimize_index.json for more details.
